Drivers who paid school-zone camera tickets during the 2024–2025 school year may be eligible for refunds after the Attorney General said the city collected fines without the required revenue-sharing agreements in place.
Illegal Right Turns: Laws, Risks, and Consequences Every Driver Should Know
Summary: Right turns feel simple, but the rules aren’t. This guide explains when a right turn becomes illegal, how enforcement works (including red light cameras), penalties, and practical tips to avoid citations and crashes.
What Counts as an Illegal Right Turn?
An illegal right turn happens any time you turn in conflict with a traffic control device, state law, or safe-yield rules. The most common situations include:
- Right on red where prohibited. A posted No Turn on Red sign makes the turn illegal at all times unless the sign lists specific hours.
- Failing to stop before turning on red. A complete stop is required in most states; “rolling” through is widely cited.
- Turning on a red arrow. A red right-turn arrow is a specific prohibition, even if other lanes have a green.
- Wrong-lane turns. Turning from a center or left lane (or a bus/right-turn-only lane) without signage allowing it.
- Turning into the wrong lane. Most laws require turning into the nearest legal lane first, then merging when safe.
- Failure to yield to pedestrians & cyclists. Crosswalk users with a walk signal and cyclists in the bike lane have priority.
State & City Differences You Should Know
Right-turn rules are similar nationwide, but local exceptions matter:
Examples
- California: Right on red permitted after a full stop unless posted otherwise; extra caution in school zones.
- New York City: Generally no right on red unless a sign explicitly permits it.
- Florida & Texas: Allowed unless posted; must stop and yield to pedestrians/bikes.
- Downtown cores: Many cities restrict right on red at high-conflict crosswalks or near transit/bike facilities.
Watch for These Signs
NO TURN ON RED(sometimes with hours)RIGHT TURN SIGNAL(turn only on green arrow)RIGHT LANE MUST TURN RIGHT(lane control)BIKES MAY USE FULL LANE/ protected bike lanes with physical barriers
If the signage seems inconsistent, follow the most restrictive control to stay safe and legal.
How Illegal Right Turns Are Enforced
1) Police Traffic Stops
Officers monitor busy intersections, school zones, work zones, and areas with heavy foot traffic. Common citations include rolling stops, turning during a red arrow, and failing to yield to pedestrians.
2) Red Light Cameras
Automated systems capture vehicles that cross the stop line during a red and then turn without stopping. Evidence typically includes still photos, video clips, lane position, and timestamps. Many programs flag “no stop” right-on-red violations specifically.
3) School Zone & Safety Corridors
Some jurisdictions add time-limited restrictions near schools or high-crash corridors. Expect stricter enforcement during posted hours and around protected bike lanes.
Common Penalties for Illegal Right Turns
Exact penalties vary by state and city, but drivers often face a combination of fines, points, and insurance impacts. School zones or red-arrow violations can carry higher fines.
| Penalty Type | What to Expect (Typical Range) |
|---|---|
| Base fine | $50–$300 depending on jurisdiction; enhanced amounts in school/construction zones. |
| License points | Often 2–3 points; may trigger administrative fees or corrective courses. |
| Court/administrative costs | Added fees can exceed the fine itself in some areas. |
| Traffic school | Sometimes offered to reduce points; availability varies. |
| Insurance impact | Premiums may rise for 1–3 years depending on your insurer and record. |
Common Misconceptions About Right Turns
Myth 1: “If it looks safe, I can always turn right on red.”
Reality: Not when signs prohibit it, a red arrow is displayed, or pedestrians/cyclists have the right of way.
Myth 2: “A rolling stop is fine if nobody’s around.”
Reality: Most laws require a full stop. Cameras routinely issue citations when wheels never fully stop.
Myth 3: “No Turn on Red is only for rush hour.”
Reality: Unless times are printed, the restriction is 24/7.
Myth 4: “I can turn from the bike lane if it’s empty.”
Reality: Using a bike lane as a turn lane is often illegal unless specifically marked.
Why Illegal Right Turns Are Dangerous
- Pedestrian conflicts: Many crashes happen when drivers look left for traffic but miss pedestrians crossing from the right.
- Right hooks with cyclists: Turning across a bike lane can cut off people on bikes who have a green or are traveling straight.
- Visibility limits: Parked vehicles, large trucks, or construction barriers create blind spots that signage is meant to mitigate.
- Intersection chaos: Wrong-lane turns and rolling stops reduce predictability and increase multi-vehicle conflicts.
How to Avoid Illegal Right-Turn Tickets (and Crashes)
- Scan for signage early. Look above, beside, and sometimes before the intersection for “No Turn on Red” or red-arrow signals.
- Come to a complete stop. Pause long enough to check crosswalks, bike lanes, and oncoming traffic—then turn when clear.
- Yield like your record depends on it. It does. Pedestrians with a walk signal and cyclists proceeding straight have priority.
- Use the correct lane. Start from the rightmost legal lane and turn into the nearest legal lane.
- Be extra cautious in school zones. Time-specific restrictions and higher fines are common.
- Follow the most restrictive control. If signage and signals feel contradictory, the strictest rule keeps you compliant.
- Maintain your brakes & tires. Good stopping power reduces the temptation to “roll” through reds.
Quick FAQ
Is right on red always legal?
No. It depends on state law and local signage. A red right-turn arrow or “No Turn on Red” sign makes it illegal, period.
Do I have to stop before turning on red?
Yes, in most states a complete stop is required before you turn right on red.
What if I turned from the middle lane?
Turning from the wrong lane is a separate violation. Expect a citation even if you stopped first.
Can cameras ticket rolling right turns?
Yes. Many systems detect when a vehicle fails to fully stop before a right on red and issue citations.
🚦 Rolling Right Turns: A Hidden Goldmine for Cities?
Are Right Turns on Red Quietly Taxing Drivers?
How Many Cities & Countries Use Red Light and Speed Cameras?
How Many Cities Use Red Light and Speed Cameras?
Automated traffic enforcement using red light and speed cameras is a growing trend worldwide, although its implementation varies significantly by region. These systems are used to deter dangerous driving behavior, improve road safety, and reduce traffic-related injuries and deaths.
Red Light Cameras in the United States
Red light cameras are currently in use in approximately 338 U.S. communities, marking a decline from the over 500 cities that operated such systems a decade ago. These programs are permitted in 22 states and the District of Columbia, with large metro areas like New York City, Chicago, Philadelphia, and Washington, D.C. leading the way.
| Rank | City | Approximate Number of Cameras | Camera Types Used | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New York City, NY | 2,200+ | Speed Cameras, Red Light | Largest U.S. program; 750 school zones covered |
| 2 | Washington, D.C. | 5,000+ | Speed Cameras, Red Light | Most traffic cameras per capita in the U.S. |
| 3 | Chicago, IL | 527+ | Speed Cameras, Red Light | Extensive program; significant revenue from fines |
| 4 | San Francisco, CA | 33+ | Speed Cameras | New program with income-based fines; 50 cameras planned |
| 5 | Los Angeles, CA | 33+ | Speed Cameras | Pilot program initiated; fines based on income |
| 6 | Philadelphia, PA | 300+ | Speed Cameras, Red Light | Focus on high-risk intersections |
| 7 | Seattle, WA | 100+ | Speed Cameras, Red Light | Active enforcement in school zones |
| 8 | Denver, CO | 100+ | Speed Cameras, Red Light | Implemented to reduce accidents |
| 9 | Phoenix, AZ | 100+ | Speed Cameras, Red Light | Comprehensive citywide coverage |
| 10 | San Diego, CA | 100+ | Speed Cameras, Red Light |
These cameras are typically placed at high-risk intersections and are credited with reducing angle collisions and red light running violations. In some areas, their effectiveness has led to a decrease in the number of cameras needed over time.
Keywords: red light camera statistics, red light enforcement USA, cities with red light cameras
Speed Cameras in the United States
Speed camera programs are in operation in about 195 U.S. cities, with legal authorization in 19 states and the District of Columbia. These cameras are often deployed in school zones, high-accident corridors, and areas where speeding is a persistent problem.
For example, New York City operates over 2,000 speed cameras near schools. Between 2019 and 2021, data showed a 73% drop in speeding violations at fixed locations, highlighting the effectiveness of the system in reducing dangerous driving.
Keywords: speed camera usage USA, speed enforcement cities, speed cameras near schools
Global Camera Use: Red Light and Speed Enforcement Worldwide
Worldwide, the number of traffic enforcement cameras far exceeds those in the U.S. Combined, there are more than 118,000 red light and speed cameras around the globe.
-
Red light cameras worldwide: Over 19,000
Speed cameras worldwide: Over 80,000
The top countries with the most traffic enforcement cameras include:
| Rank | Country | Red Light Cameras | Speed Cameras | Total Cameras |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brazil | 1,170 | 14,210 | 15,380 |
| 2 | Italy | 2,321 | 8,104 | 10,425 |
| 3 | United States | 3,974 | 4,001 | 7,975 |
| 4 | United Kingdom | 811 | 4,004 | 4,815 |
| 5 | Germany | 408 | 3,869 | 4,277 |
| 6 | France | 720 | 2,969 | 3,689 |
| 7 | United Arab Emirates | 482 | 2,109 | 2,591 |
| 8 | Sweden | 0 | 2,487 | 2,487 |
| 9 | Spain | 377 | 1,598 | 1,975 |
| 10 | Turkey | 70 | 1,427 | 1,497 |
| 11 | Austria | 177 | 1,245 | 1,422 |
| 12 | Argentina | 470 | 772 | 1,242 |
| 13 | Belgium | 68 | 1,163 | 1,231 |
| 14 | Finland | 45 | 1,057 | 1,102 |
| 15 | Canada | 774 | 279 | 1,053 |
| 16 | Taiwan | 308 | 712 | 1,020 |
| 17 | Poland | 208 | 534 | 742 |
| 18 | Australia | 335 | 264 | 599 |
| 19 | Morocco | 7 | 548 | 555 |
| 20 | Croatia | 12 | 513 | 525 |
This shows a strong global commitment to improving traffic safety through automated enforcement.
Keywords: global red light camera statistics, worldwide speed camera data, countries with most speed cameras
Legal and Policy Differences
In the U.S., state-level laws govern whether red light and speed cameras can be used. While some states fully embrace these systems, others have banned or heavily restricted them. For example, Texas has prohibited red light cameras, although some cities were allowed to maintain them until contracts expired.
These legal differences make the U.S. a patchwork of enforcement zones, where drivers may face automatic fines in one state but not the next.
Keywords: red light camera laws by state, speed camera legal states, U.S. automated enforcement laws
Conclusion
Red light and speed cameras continue to play a major role in promoting road safety in the U.S. and around the world. While their use is growing globally, adoption in the U.S. remains dependent on local and state policy. Cities that do use these systems have often seen measurable improvements in driver behavior and road safety.
Keywords summary: how many cities use red light cameras, speed camera statistics USA, red light enforcement worldwide, traffic camera usage by country
Which U.S. Cities Offer Reduced Traffic Ticket Fines for Low-Income Drivers?
Traffic tickets can impose significant financial burdens on low-income individuals, potentially leading to escalating fines, license suspensions, and other legal challenges. Recognizing this, several U.S. cities have implemented programs to reduce or waive traffic ticket costs for low-income drivers, promoting fairness and equity in the justice system.
Why Cities Are Reducing Fines for Low-Income Drivers
Flat-rate fines disproportionately impact those with limited incomes. A $200 ticket may be manageable for some but can be devastating for others living paycheck to paycheck. To address this disparity, cities are adopting income-based payment models, amnesty programs, and alternative sentencing options to make traffic enforcement more equitable.
Cities Offering Reduced Traffic Ticket Fines Based on Income
1. San Francisco, California
San Francisco has been a pioneer in reforming fines and fees. The city implemented recommendations from its Fines and Fees Task Force to reduce financial penalties for low-income residents. Programs include income-based payment plans and the ability to perform community service in lieu of payment.
2. Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., has introduced several initiatives to alleviate the burden of traffic fines on low-income residents:
-
Community Service Debt Repayment Program: Under the Traffic and Parking Ticket Penalty Amendment Act of 2018, low-income residents (those earning at or below 250% of the federal poverty level) can reduce their civil fines by performing community service. Each hour of service performed reduces the amount owed by an amount equivalent to the District's minimum hourly wage.
-
Automated Traffic Enforcement Equity (ATEquity) Pilot: Launched in 2023, this pilot program allows SNAP (food stamps) recipients to apply for a 50% reduction on one eligible camera ticket (valued at $100 or less) issued within the past 30 days. The program aims to assess the impact of income-based fine reductions on payment rates and future violations.
-
Ticket Amnesty Programs: D.C. has periodically offered amnesty programs, allowing drivers to pay outstanding tickets without additional penalties. For instance, a program running from June to September 2021 enabled drivers to pay the original ticket amounts without late fees, resulting in over 25,500 people settling their debts and approximately $36.2 million in paid fines.
3. Seattle, Washington
Seattle offers Debt Reduction Hearings for low-income individuals unable to pay overdue parking and traffic ticket fines. Eligible participants can request reductions or waivers based on financial hardship.
4. Los Angeles, California
Set to launch in 2026, Los Angeles plans to implement an income-based traffic fine system similar to San Francisco's, offering community service as an alternative for low-income offenders.
5. Chicago, Illinois
Chicago has introduced the Clear Path Relief Pilot Program, allowing residents earning less than 300% of the federal poverty level to pay half the rate for city-issued traffic fines on non-parking meter tickets. The program also offers debt relief options for eligible participants.
6. Minnesota
Minnesota has enacted the Lights On program, replacing traffic tickets for broken headlights and tail lights with vouchers for low-income drivers. These vouchers, worth up to $250, can be redeemed at participating repair shops to cover the costs of repairs.
7. Kansas
Kansas has passed a new law aimed at addressing the financial burden of drivers facing multiple fines and fees. Effective January 2025, the law reduces license reinstatement fees to a single $100 charge, regardless of the number of tickets. It also allows judges to determine when to reinstate a license and reduce fines and fees.
8. El Paso, Texas
El Paso's Municipal Court offers periodic amnesty programs, waiving warrant and collection fees for delinquent tickets. For example, the 2025 program ran from February 17 to March 8, allowing residents to settle outstanding citations without additional penalties .El Paso Texas
9. Highland Park, Michigan
In Highland Park, a traffic amnesty program waives fees on outstanding tickets, enabling residents to pay reduced amounts and clear their driving records. The initiative aims to assist individuals in resolving long-standing fines and restoring their driving privileges. FOX 2 Detroit+1FOX 5 Atlanta+1
10. Fulton County, Georgia
Fulton County has launched a traffic ticket amnesty program offering up to 80% reductions on fines for eligible offenses. The program focuses on non-violent infractions and aims to help residents restore their driving records and avoid further legal complications.FOX 5 Atlanta
Conclusion
Cities across the United States are recognizing the disproportionate impact of traffic fines on low-income individuals and are implementing programs to address this issue. By offering income-based reductions, community service alternatives, and amnesty initiatives, these cities aim to create a more equitable system that acknowledges the financial disparities among residents.
Photo Enforcement Ballot Measures: Why They Have Never Survived a Public Vote
As cities across the United States grapple with issues of traffic safety and enforcement, photo enforcement measures—such as red-light and speed cameras—have emerged as potential solutions. However, attempts to implement these measures through public ballot initiatives have consistently failed to gain voter approval. This article explores the reasons behind the public's resistance to photo enforcement ballot measures, notable examples of failed initiatives, the implications for traffic safety, and what it means for the future of automated enforcement.
Understanding Photo Enforcement
Photo enforcement refers to the use of automated systems to capture images of vehicles that violate traffic laws, such as running red lights or speeding. While proponents argue that these systems enhance safety and reduce traffic violations, public sentiment has often leaned against their implementation through ballot measures.
Historical Context: Failed Ballot Measures
-
Voter Concerns About Privacy: One of the primary reasons photo enforcement ballot measures have struggled to survive public votes is widespread concern about privacy. Many voters fear that the increased use of surveillance cameras could lead to an infringement on personal freedoms and privacy rights. This sentiment often outweighs arguments about the potential safety benefits.
-
Perception of Revenue Generation: Voters frequently view photo enforcement as a revenue-generating scheme rather than a genuine safety initiative. When the public perceives that a measure is primarily designed to generate income for the city rather than improve safety, they are less likely to support it. The fear of "money traps," where municipalities profit from traffic violations, can lead to strong opposition.
-
Distrust of Government Motives: Distrust in government agencies can play a significant role in public sentiment against photo enforcement measures. Voters may question the transparency and accountability of how funds generated from fines would be used, leading to skepticism about the overall intent behind the ballot measures.
-
Concerns About Effectiveness: Critics of photo enforcement often argue that these systems do not effectively reduce accidents or improve traffic safety. Instead, they claim that such measures merely displace accidents rather than prevent them. This belief can significantly impact voter support when considering the implementation of these systems.
-
Successful Campaigns Against Initiatives: In various jurisdictions, organized campaigns have successfully mobilized public opposition against photo enforcement ballot measures. These campaigns often highlight the drawbacks and potential negative consequences of automated enforcement, swaying public opinion against the proposals.
Notable Examples of Failed Ballot Measures
-
San Francisco Proposition G (2010): This measure aimed to authorize the city to use speed cameras in specific locations to combat speeding and improve road safety. Despite support from some city officials and traffic safety advocates, it was met with strong opposition from civil liberties groups and ultimately failed in the ballot, reflecting the public's concerns about surveillance and privacy.
-
Red Light Camera Measures in Los Angeles (Various Years): Over the years, several proposals to expand the use of red-light cameras in Los Angeles have faced rejection at the polls. Voters expressed concerns about the perceived focus on revenue generation over public safety and the effectiveness of such measures in reducing traffic violations.
-
Arizona Red-Light Camera Initiative (2010): Arizona residents voted on a ballot measure that sought to expand red-light camera use throughout the state. However, the initiative was met with opposition due to fears about privacy, government surveillance, and the financial motivations behind the program, leading to its failure.
Implications for Traffic Safety
The failure of photo enforcement ballot measures to gain public support has significant implications for traffic safety efforts. Without these systems, cities may struggle to find effective alternatives to address speeding and reckless driving, leading to continued accidents and fatalities on the roads.
In the absence of photo enforcement, law enforcement agencies may need to allocate more resources to traditional policing methods, which can strain budgets and manpower. Moreover, without automated enforcement systems, the opportunity for consistent and fair traffic law enforcement may diminish, creating inequities in how traffic violations are addressed.
The Future of Photo Enforcement Initiatives
Given the history of failed public votes, cities considering photo enforcement must find new ways to engage with the community and build trust. Here are some strategies that could improve public perception and potentially lead to successful ballot measures in the future:
-
Public Education Campaigns: Effective communication about the benefits of photo enforcement and how it can enhance safety is essential. Engaging community members through educational campaigns can help alleviate fears and address concerns.
-
Transparent Use of Funds: Clearly outlining how revenue from photo enforcement will be allocated can help build trust with the public. Demonstrating a commitment to reinvesting funds into community safety initiatives may increase voter support.
-
Pilot Programs: Implementing pilot programs that demonstrate the effectiveness of photo enforcement in reducing accidents and improving safety can provide valuable data and build public trust. Success stories from other jurisdictions can also bolster community confidence in these measures.
- In Mukilteo, Washington 70% of the voters banned the cameras and in Anaheim, California 73% voted against them.
- Earlier in 2010, 61% of Sykesville, Maryland voters overturned a speed camera ordinance. In 2009, 86% of Sulphur, Louisiana rejected speed cameras.
- The November 2009 elections included three votes: 72% said no in Chillicothe, Ohio; Heath, Ohio, and College Station,
- Texas also rejected cameras. In 2008, residents in Cincinnati, Ohio rejected red light cameras. 66% of Steubenville
- Ohio voters rejected photo radar in 2006. In the 1990s, speed cameras lost by 66% of the vote in Peoria, Arizona, and Batavia, Illinois.
- In 1997, voters in Anchorage, Alaska banned cameras even after the local authorities had removed them. In 2003, 64% of voters in Arlington, Texas voted down "traffic management cameras" that opponents at the time said could be converted into ticketing cameras.
Conclusion
While photo enforcement ballot measures have yet to gain traction in public votes, understanding the underlying concerns can help cities refine their approaches to traffic safety. By addressing privacy concerns, ensuring transparency, and engaging communities effectively, cities like San Francisco, Oakland, and San Jose may find a path toward successful implementation of photo enforcement initiatives in the future. As public safety remains a top priority, the conversation around photo enforcement will undoubtedly continue, shaping the landscape of traffic enforcement across the country.
Updated Red Light and Speed Camera Fine Information by State
As a driver, understanding the laws and fines associated with red light cameras and speed cameras is crucial for maintaining good driving habits and avoiding unexpected expenses. This article provides an updated overview of the fines and points associated with red light and speed camera violations across the United States. Please note that these fines can vary by municipality, so it’s essential to check local regulations for the most accurate information.
Red Light Camera Fines and Points
The table below summarizes the current fines and points for red light camera violations in each state:
| State | Red Light Camera Fine ($) | Red Light Camera Points |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $100 | No Points |
| Arizona | $165-$250 | 2 Points |
| Arkansas | No Programs | - |
| California | $490 | 1 Point |
| Colorado | $40-$80 | 4 Points |
| Delaware | $75-$230 | - |
| District of Columbia | $150 | 0 to 2 Points |
| Florida | $200 | - |
| Georgia | $70 | No Points |
| Hawaii | $77 | - |
| Illinois | $100-$500 | 20 Points |
| Indiana | No Programs | - |
| Iowa | $45-$150 | - |
| Kansas | No Programs | - |
| Louisiana | $100-$140 | No Points |
| Maryland | $100 | No Points |
| Michigan | No Programs | - |
| Minnesota | No Programs | - |
| Mississippi | No Programs | - |
| Missouri | $100 | - |
| Nevada | No Programs | - |
| New Jersey | $85 | No Points |
| New Mexico | $75 | - |
| New York | $50-$100 | No Points |
| North Carolina | $50-$100 | 3 Points |
| Ohio | $100-$200 | - |
| Oklahoma | No Programs | - |
| Oregon | $260-$1,000 | - |
| Pennsylvania | $100 | No Points |
| Rhode Island | $75 | - |
| South Dakota | No Programs | - |
| Tennessee | $50 | No Points |
| Texas | State Ban | - |
| Virginia | $100-$200 | 0 to 4 Points |
| Washington | $124-$250 | No Points |
| West Virginia | No Programs | - |
| Wisconsin | No Programs | - |
Speed Camera Fines and Points
In addition to red light cameras, many states also have speed camera programs. Below is a summary of speed camera fines and points across the states:
| State | Speed Camera Fine ($) | Speed Camera Points |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | - | - |
| Arizona | $165-$250 | 2 Points |
| Arkansas | - | - |
| California | - | - |
| Colorado | $40-$80 | 4 Points |
| Delaware | - | - |
| District of Columbia | $50-$300 | 0, 3, 4, 5 Points |
| Florida | - | - |
| Georgia | - | - |
| Hawaii | - | - |
| Illinois | $250-$500 | 20 Points |
| Indiana | No Programs | - |
| Iowa | $45-$150 | - |
| Kansas | No Programs | - |
| Louisiana | - | - |
| Maryland | $40-$1,000 | No Points |
| Michigan | No Programs | - |
| Minnesota | No Programs | - |
| Mississippi | No Programs | - |
| Missouri | - | - |
| Nevada | No Programs | - |
| New Jersey | - | - |
| New Mexico | $75 | - |
| New York | $90-$1,200 | No Points (Possible Jail Time) |
| North Carolina | - | - |
| Ohio | $100-$200 | - |
| Oklahoma | No Programs | - |
| Oregon | $110-$2,000 | - |
| Pennsylvania | - | - |
| Rhode Island | - | - |
| South Dakota | No Programs | - |
| Tennessee | $50 | No Points |
| Texas | - | - |
| Virginia | - | - |
| Washington | $124-$250 | No Points |
| West Virginia | No Programs | - |
| Wisconsin | No Programs | - |
Important Notes
-
Local Variations: Keep in mind that this information can vary widely by municipality within each state. It’s essential to verify specific details with local laws or law enforcement agencies.
-
Changes in Regulations: Traffic laws and fines can change frequently. Drivers should regularly check for updates in their state or locality to stay informed.
-
Safe Driving Practices: To avoid the potential of incurring fines or points on your license, always adhere to traffic signals and speed limits, and practice safe driving habits.
By understanding the fines and points associated with red light and speed camera violations in your state, you can better navigate the roads and make informed decisions as a driver. Always stay updated on your local traffic laws to ensure a safe and compliant driving experience.
Cedar Rapids Mobile Speed Cameras
Cedar Rapids, Iowa, has taken significant strides to improve road safety through the implementation of mobile speed cameras. These devices play a crucial role in monitoring traffic speeds, deterring reckless driving, and ultimately reducing accidents. In this article, we’ll explore how Cedar Rapids mobile speed cameras work, their impact on community safety, and important information for residents and drivers.
What Are Mobile Speed Cameras?
Mobile speed cameras are portable devices deployed by law enforcement agencies to monitor vehicle speeds in various locations. Unlike fixed speed cameras, which are permanently installed, mobile cameras can be easily moved to different sites throughout Cedar Rapids, allowing for flexible enforcement of speed limits where they are most needed.
How Cedar Rapids Mobile Speed Cameras Operate
-
Identification of High-Risk Areas: Cedar Rapids authorities analyze traffic patterns and accident data to identify locations with high instances of speeding and accidents. Mobile speed cameras are then strategically placed in these areas.
-
Speed Monitoring: When a vehicle exceeds the designated speed limit, the mobile speed camera captures an image of the vehicle along with its speed. The system is designed to ensure accuracy and minimize false readings.
-
Issuance of Citations: If a driver is photographed exceeding the speed limit, a citation is issued. The citation typically includes details such as the vehicle’s speed, the location, and a photograph of the vehicle.
Benefits of Mobile Speed Cameras
-
Deterrence of Speeding: The presence of mobile speed cameras serves as a deterrent for drivers, encouraging them to adhere to posted speed limits. Studies have shown that simply knowing there is a chance of being monitored reduces speeding behavior.
-
Reduction in Traffic Accidents: With lower speeds, the likelihood of accidents decreases. The goal of Cedar Rapids’ mobile speed camera program is to enhance safety for all road users, including pedestrians and cyclists.
-
Flexibility and Responsiveness: Mobile cameras can be moved to different locations based on real-time data, allowing law enforcement to address emerging traffic issues swiftly. This flexibility ensures that enforcement efforts are directed where they are needed most.
-
Cost-Effective Enforcement: Mobile speed cameras can be a cost-effective tool for traffic enforcement. They reduce the need for continuous police presence while still effectively monitoring speeds and promoting compliance with traffic laws.
Public Response and Community Impact
The introduction of mobile speed cameras in Cedar Rapids has received mixed responses from the public. Many residents appreciate the enhanced safety measures, especially in high-traffic areas where speeding has been a concern. Others express frustration over the perceived intrusive nature of surveillance.
City officials aim to balance these concerns by ensuring that the program is transparent and focused on improving safety rather than merely generating revenue. Public education campaigns often accompany the implementation of mobile speed cameras, informing drivers about the program’s objectives and emphasizing the importance of road safety.
Tips for Drivers in Cedar Rapids
To avoid citations from mobile speed cameras and ensure safety on the roads, drivers in Cedar Rapids should:
-
Know the Speed Limits: Familiarize yourself with speed limits in different areas, especially in school zones or residential neighborhoods where limits may be lower.
-
Stay Aware of Your Speed: Regularly check your speedometer and adjust your speed accordingly. Utilize cruise control on highways to maintain a consistent speed.
-
Look for Signs: Watch for signs indicating areas where mobile speed cameras may be in operation. These signs can serve as a reminder to adhere to speed limits.
-
Be Informed: Stay updated on the locations where mobile speed cameras are being deployed. Local news outlets and the city’s official website often provide information about active camera sites.
Conclusion
Cedar Rapids mobile speed cameras represent a proactive approach to enhancing road safety and reducing traffic violations. By understanding how these cameras operate and their benefits to the community, residents and drivers can work together to promote safer roadways. Whether you are a local resident or just passing through, being aware of mobile speed camera enforcement can help ensure that you drive responsibly and contribute to a safer Cedar Rapids for everyone.
Call to Action
For more information about Cedar Rapids mobile speed cameras, including updates on locations and safety tips, visit the city’s official website or follow local news sources. Let’s keep our roads safe together!
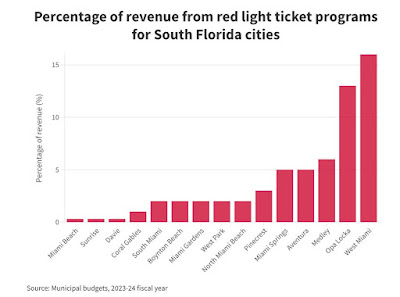
The State of Florida Seeks Share of City Revenue from Cameras
Florida cities have long used red light cameras as a tool to promote traffic safety and reduce violations at dangerous intersections. These cameras generate significant revenue for local governments, funding various public services. However, the State of Florida is increasingly interested in obtaining a portion of this income, raising questions about the impact on local budgets and public safety initiatives. Here’s a look at why the state wants a share of red light camera revenue, what it means for Florida cities, and how it could affect residents.
Why Does Florida Want Red Light Camera Revenue?
Utilities for Unpaid Offenders Shut Off: What You Need to Know
In a growing trend across the United States, several cities and utility companies are implementing policies that allow them to shut off essential services, such as water, electricity, and gas, for individuals who fail to pay fines related to traffic violations, including red light and speed camera tickets. This controversial practice raises important questions about the balance between enforcing traffic laws and ensuring access to essential services. Here’s what you need to know about these policies and their implications for offenders.
Why Are Utilities Shut Off for Unpaid Offenders?
The rationale behind shutting off utilities for unpaid offenders centers on several key factors:
-
Revenue Generation: Municipalities often face budget constraints, and unpaid fines can significantly impact their financial health. Shutting off utilities serves as a method to collect outstanding debts.
-
Encouraging Compliance: By threatening essential services, cities hope to encourage offenders to pay their fines promptly and deter future violations. The idea is that the potential loss of utilities will motivate individuals to fulfill their financial obligations.
-
Addressing Public Safety: Some argue that ensuring compliance with traffic laws through stricter penalties, including utility shutoffs, enhances overall public safety. The rationale is that enforcing consequences for violations can lead to more responsible driving behavior.
The Controversy Surrounding Utility Shutoffs
While the policies may be intended to improve compliance and generate revenue, they are not without controversy. Key concerns include:
-
Impact on Vulnerable Populations: Shutting off utilities can disproportionately affect low-income individuals and families who may already be struggling to make ends meet. Losing access to water or electricity can create significant hardships, including health and safety risks.
-
Legal and Ethical Questions: Critics argue that punishing individuals for unpaid fines by cutting off essential services raises ethical questions. Is it fair to deny basic necessities as a means of enforcing traffic laws? Additionally, legal challenges may arise regarding the legality of such practices.
-
Ineffective Deterrence: Some studies suggest that harsh penalties, such as utility shutoffs, may not effectively deter future violations. Offenders might simply accumulate more debt rather than changing their behavior.
What Offenders Should Know
If you are facing unpaid fines that could lead to utility shutoffs, here are some steps to consider:
-
Address the Fines Promptly: If you receive a ticket, it’s crucial to address it as soon as possible. Ignoring the issue can lead to increased fines, additional penalties, and potential utility shutoffs.
-
Explore Payment Plans: Many jurisdictions offer payment plans or hardship programs for individuals struggling to pay fines. Contact the issuing authority to discuss your options.
-
Stay Informed About Local Policies: Keep abreast of local policies regarding unpaid fines and utility shutoffs. This will help you understand your rights and responsibilities.
-
Seek Legal Advice: If you believe that a utility shutoff is unfair or unlawful, consider consulting a legal expert. They can help you navigate the legal landscape and explore options for contesting fines or avoiding utility shutoffs.
Conclusion
The practice of shutting off utilities for unpaid traffic violations is a growing trend that raises important questions about fairness, legality, and public safety. While municipalities seek to enforce compliance and generate revenue, it’s crucial to consider the implications for vulnerable populations and the potential ineffectiveness of such measures. For individuals facing unpaid fines, addressing the issue promptly and exploring available options can help prevent severe consequences, including utility shutoff.
Florida Red Light Camera Fines Increasing: What Drivers Need to Know
In recent years, red light cameras have become a common feature at intersections throughout Florida. While they aim to enhance road safety by discouraging reckless driving, recent changes in fines associated with red light camera violations are raising eyebrows among motorists. This article outlines the upcoming increases in red light camera fines in Florida and provides essential information for drivers to navigate this evolving landscape.
Understanding Red Light Cameras in Florida
Red light cameras are automated systems installed at intersections to capture images of vehicles that run red lights. The primary goal is to reduce traffic accidents and enhance safety for drivers, passengers, and pedestrians. However, violating a red light can result in significant financial penalties, which are now set to rise.
Recent Increases in Fines
The Florida Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles has announced that fines for red light camera violations will be increasing starting in [insert specific month/year, if known]. The new fines will vary depending on the violation but could reach up to $200 for certain infractions, with additional fees that may apply. This change is part of an ongoing effort to ensure compliance with traffic laws and promote safer driving behaviors.
Current Fines vs. New Fines
Currently, the fines for red light camera violations in Florida typically range from $158 to $200. Under the new structure, the fines are expected to increase significantly, with some municipalities implementing fines as high as $250.
| Violation | Current Fine ($) | New Fine ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Running a red light | $158 | $200-$250 |
| Failure to stop for a red light | $158 | $200-$250 |
Note: Always check with local authorities for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding fines.
Points and Consequences
In addition to fines, drivers who receive a red light camera ticket in Florida may also incur points on their driving record. Typically, violations result in 3 points, which can lead to increased insurance premiums and potential repercussions if points accumulate.
Implications for Drivers
-
Increased Financial Burden: With fines set to rise, drivers must be more cautious at intersections equipped with red light cameras. A violation could lead to a hefty fine that impacts your budget.
-
Impact on Insurance: Accumulating points can result in higher insurance premiums. Maintaining a clean driving record is essential to avoid financial repercussions.
-
Local Variations: Fines and enforcement practices may vary by municipality, making it crucial for drivers to stay informed about the rules in their area.
Tips for Avoiding Red Light Camera Violations
To avoid falling victim to increased fines, consider the following tips:
-
Stay Alert: Always be aware of traffic signals and the posted speed limits.
-
Stop on Yellow: When approaching an intersection, prepare to stop if the light turns yellow. A sudden stop is better than a late decision to run the red light.
-
Know Your Area: Familiarize yourself with intersections that have red light cameras. Being aware can help you drive more cautiously.
-
Practice Defensive Driving: Anticipate the actions of other drivers, especially at busy intersections.
Conclusion
With Florida set to increase red light camera fines, drivers need to be proactive in understanding the new rules and adjusting their driving habits accordingly. By staying informed and practicing safe driving techniques, you can avoid the financial burden and potential legal consequences associated with red light camera violations. Always check with local law enforcement for the most current information on traffic laws and fines in your area to stay ahead of the curve.
Verra Mobility (VRRM) Stock Hits All Time Highs
Verra Mobility (ticker symbol VRRM) is a company that specializes in technology solutions for the transportation industry, including tolling, red-light enforcement, and traffic management. If the stock hit all-time highs, it suggests that the company's performance and investor sentiment have been positive, driving the stock price to new records.
Illinois Legislation Proposing Trial by Phone: A New Era in Court Proceedings
In an effort to modernize the judicial system and enhance accessibility, Illinois legislators have introduced a groundbreaking proposal to allow trials to be conducted via phone. This innovative approach aims to streamline court processes, reduce backlogs, and improve the overall efficiency of the legal system. As courts adapt to the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic and embrace technological advancements, this legislation could set a precedent for other states. Here’s what you need to know about the proposed trial by phone legislation in Illinois.
The Need for Change in the Judicial System
The traditional court system has faced numerous challenges in recent years, including:
-
Backlogs and Delays: Courts across Illinois have struggled with significant backlogs, leading to lengthy delays in legal proceedings. This has affected the timely resolution of cases and has often left defendants waiting months or even years for their day in court.
-
Accessibility Issues: Many individuals, particularly those in rural areas or with mobility challenges, find it difficult to attend court hearings. Travel time, transportation costs, and other barriers can prevent people from accessing justice.
-
Technological Advancements: The pandemic accelerated the adoption of technology in various sectors, including the legal field. Virtual court proceedings became a necessity, demonstrating that remote participation could be effective in many situations.
Key Features of the Proposed Legislation
The Illinois legislation proposing trial by phone includes several key features:
-
Remote Participation: Defendants, attorneys, and witnesses would have the option to participate in court proceedings via phone. This would allow for greater flexibility and accessibility, particularly for those unable to attend in person.
-
Limited to Certain Cases: The proposal is likely to focus on specific types of cases, such as minor traffic violations or low-level misdemeanors, where a phone trial could be appropriate without compromising the integrity of the judicial process.
-
Procedural Safeguards: The legislation would include procedural safeguards to ensure that the rights of all parties are protected. This may involve recording the proceedings, ensuring secure communication channels, and providing options for in-person hearings if necessary.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: By reducing the need for in-person appearances, the legislation aims to cut down on court costs, transportation expenses, and lost work time for participants.
Potential Benefits of Trial by Phone
The proposed legislation offers several potential benefits:
-
Increased Accessibility: By allowing trials to be conducted via phone, individuals who may have difficulty attending court in person can participate more easily, promoting fairness and inclusivity in the legal process.
-
Reduced Backlogs: Remote trials could help alleviate court backlogs, enabling cases to be resolved more swiftly and efficiently. This would benefit not only defendants but also the judicial system as a whole.
-
Flexibility for Legal Professionals: Attorneys and legal representatives would have greater flexibility in managing their schedules, allowing them to handle more cases effectively.
-
Adaptability to Future Challenges: As society continues to adapt to technological advancements, implementing phone trials positions the Illinois judicial system to respond to future challenges, whether they be health-related or logistical.
Challenges and Considerations
While the proposal presents many advantages, there are also challenges to consider:
-
Ensuring Fairness: Critics may raise concerns about ensuring fair trials and the ability to adequately present evidence over the phone. Safeguards will be necessary to maintain the integrity of the judicial process.
-
Technical Issues: Reliance on technology means that courts must be prepared to address potential technical issues that could disrupt proceedings or affect communication.
-
Public Perception: The perception of phone trials as a less formal or serious approach to justice may lead to resistance from some legal professionals or the public.
Conclusion
The proposed legislation in Illinois to allow trials by phone marks a significant step towards modernizing the judicial system and increasing accessibility. By leveraging technology, the state aims to address long-standing challenges in the legal process while ensuring that justice remains accessible to all. As the legislation progresses, it will be crucial for lawmakers, legal professionals, and the public to engage in discussions about its implications and to work together to create a system that serves the needs of all citizens effectively.
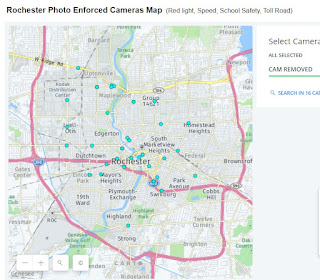
Map of Rochester, New York Red Light Cameras Removed
Queensland, Australia Is Increasing Speeding & Red Light Fines
| Offense | Penalty |
|---|---|
| 1-10km/h over the speed limit | $287 and one demerit point |
| 11-20km/h over the speed limit | $431 and three demerit points |
| 21-30km/h over the speed limit | $646 and four demerit points |
| 31-40km/h over the speed limit | $1078 and six demerit points |
| Over 40km/h above the speed limit | $1653, eight demerit points, and a six-month license suspension |
| Running a red light | $575 and three demerit points |
The number of road safety cameras continues to increase in Queensland, and they’ve been busy in the last 12 months.
Based on the number of infringement notices issued, the top five fixed and mobile speed camera locations are all located in the most populous part of the state, the south-east, and all but one is located in Brisbane.
As of March 2022, Queensland’s camera network includes the following:
- 21 fixed speed cameras
- 48 fixed speed and red light camera locations
- 113 fixed red light cameras
- 9 point-to-point cameras
| Location | Type | Number of notices issued |
|---|---|---|
| Pacific Motorway, Loganholme | Speed | 16,295 |
| Intersection of Mt Gravatt-Capalaba Road and Gateway Motorway, MacKenzie | Red light and speed | 14,440, including 396 red light notices |
| Intersection of Smith Street and Kumbari Avenue, Southport | Red light and speed | 13,881, including 151 red light notices |
| Main Street, Kangaroo Point | Speed | 13,694 |
| Intersection of Lutwyche Road and Kedron Park Road, Kedron | Red light and speed | 12,824, including 578 red light notices |
| Location | Number of notices issued |
|---|---|
| Hale Street, Petrie Terrace/Paddington | 11,213 |
| Ipswich Road, Annerley | 8432 |
| Southern Cross Way, Eagle Farm | 4967 |
| Mt Gravatt-Capalaba Road, Upper Mount Gravatt | 4139 |
| Herston Road, Kelvin Grove | 4078 |
California Red Light Camera Ticket Facts
Running a stop sign or red light in California usually results in a fine and demerit points on your driving record. Many areas around California now have red light cameras in place to catch lawbreakers. When you receive one of these red light camera tickets, it's critical that you answer appropriately and quickly.
Here are five things you should know about California red light camera tickets so you can be prepared if you get one.
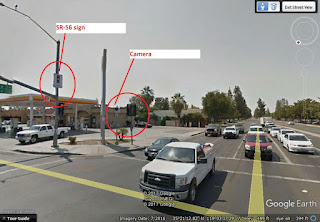
1. Sensors cause red light camera tickets to be issued.
When a vehicle passes over a sensor when the light is red in an intersection in Los Angeles and most other cities in California, a red-light ticket is issued. The camera then takes a picture of the vehicle's license plate as well as the driver. Because the camera flashes will go off as you travel through the intersection, you may see that you've been caught running a red light by a camera. A traffic ticket will be mailed to the vehicle's registered owner. The fine amount, visual proof, a copy of the traffic citation, and information on how to dispute the ticket will all be included with the ticket.
2. Red light cameras are operated by companies operating outside of California
Outside corporations, not the city, install and operate the bulk of red light camera systems in California. As a result, these businesses are compelled to issue tickets to drivers. Vehicle owners may receive unjustified tickets because they are contractually compelled to achieve a minimum number of recorded offenses.
3. What is the fine for running a photo enforced red light in California?
The amount of fines a driver has to pay for California traffic violations include a base fine plus a number of fees and surcharges, which can substantially increase the total fine amount. The fees and surcharges are a variable, but you can count on the base fine as the standard starting point.
The following are the base fines in California for infractions of stoplights and stop signs:
- Running right through a solid or flashing red light will get you $490 for running red lights.
- Making an unlawful right turn at a red light costs $250
- The average fine for rolling through a stop sign is $250 in California.
4. Do I get any points for a red light camera violation in California?
Californians should be informed that, in addition to the fines connected with stop light and stop sign infractions, each of these will result in one point being added to their driving records. A license suspension can result from accumulating too many points. Fortunately, completing a course at a California traffic school can help you avoid a red light violation.
Drivers should also be aware that, depending on the circumstances of the offense, a red light or stop sign violation could result in a reckless driving conviction. In the worst-case scenario, a driver could be charged with vehicular manslaughter if one of these violations results in the death of another person.
5. Can I get the ticket dismissed, lowered, or ignore the citation received in the mail?
You should be aware of the following critical red light ticket factors:
- Some red light tickets are issued by mistake, such as when you make a right-hand turn on red without first coming to a complete stop.
- You may also not be the driver of the vehicle.
- You may be able to keep points off your record or seek to have the fine reduced depending on the type of infraction. To find out, contact someone who knows, such as an attorney or an online traffic school.
- According to California law, a citation for a red light camera infraction can only be issued if the driver and license plate are clearly visible.
- Not all red light camera tickets require you to take action or come with consequences if you don't pay the fine.
If you receive a red light camera ticket in California, the first line of defense is to become knowledgeable.